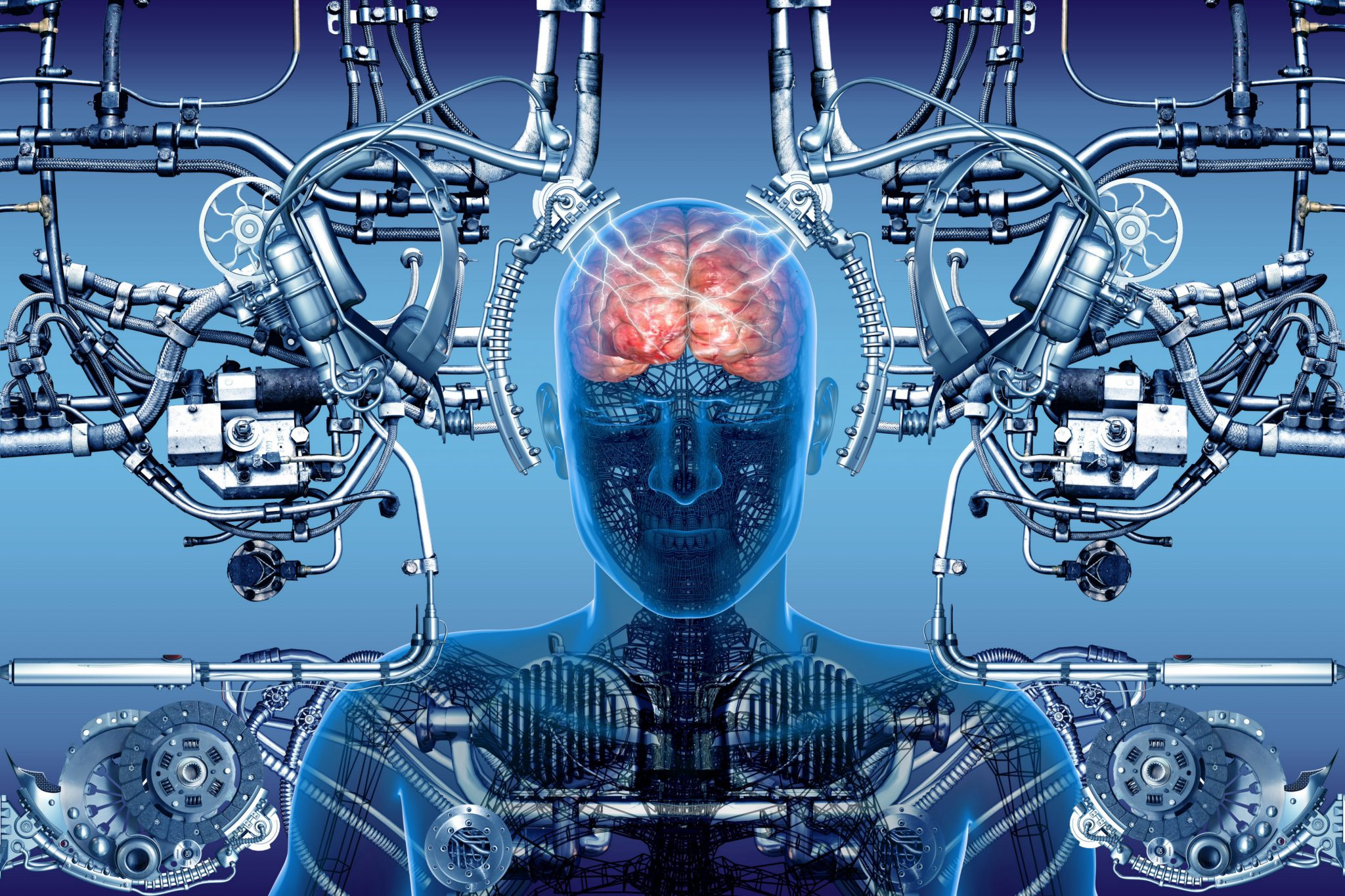
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) represent a groundbreaking intersection of technology and neuroscience, promising to revolutionize how individuals interact with the digital world. By translating thought directly into action, BCI technology is paving the way for incredible advancements in neurotechnology, especially for those with physical disabilities. With the introduction of devices like brain chips, users can control computers and prosthetic limbs using only their minds, a development that could be life-changing for millions. However, along with this unprecedented potential comes a suite of ethical concerns, including issues surrounding mental privacy and the darker implications of mind control. As we delve deeper into the capabilities and consequences of these innovations, it is essential that we tread carefully to ensure that this powerful technology serves to empower, rather than manipulate.
Also known as neural interfaces, brain-machine interfaces (BMIs) are part of a cutting-edge field that is pushing the boundaries of human augmentation and interaction with technology. These advanced systems meld the human brain with computer systems, enabling unprecedented control over devices and offering new solutions for medical challenges. While the potential of these innovative systems for enhancing human capability is immense, they also raise significant questions about the ethical implications of interfacing human cognition with machines. Concerns about mental privacy and potential abuses of mind influence highlight the urgent need for comprehensive regulations and ethical guidelines in this emerging domain. As we explore the future of neural connectivity, striking the right balance between innovation and responsibility will be critical to ensuring these developments benefit humanity at large.
The Rise of Brain-Computer Interfaces: A New Era in Neurotechnology
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) represent a groundbreaking stride in neurotechnology, allowing users to communicate with devices using only their thoughts. This innovation holds promise for individuals with severe disabilities, providing them the ability to control wheelchairs, prosthetic limbs, and even computers seamlessly. As exemplified by Noland Arbaugh’s experience after his Neuralink implant, BCIs can enable paralyzed individuals to interact with the digital world in ways previously thought impossible. The potential applications of BCI technology extend beyond just mobility aids; they could revolutionize communication for those who are non-verbal, enhancing their quality of life significantly.
However, the rapid advancement of BCI technology raises essential questions about its implications for mental privacy. The ability to decode thoughts could lead to situations where personal information is accessed without consent, echoing concerns from psychological experiments of the past. As neurotechnology develops, maintaining robust safeguards to protect individual autonomy and personal data becomes increasingly crucial. The challenge will be to harness the benefits of brain chips while preventing misuse that could intrude upon mental privacy.
Ethical Implications of Neurotechnology in the Age of Mind Control
The intersection of brain-computer interfaces and ethical considerations invites a critical examination of potential abuses of power. The historical examples drawn from the CIA’s MKUltra program illustrate a dark chapter in American history where psychological manipulation was experimented upon unsuspecting individuals. As Lukas Meier notes, the capabilities that BCIs possess could inadvertently facilitate the same type of behavior control that was explored during the Cold War. In a world increasingly reliant on neurotechnology, it’s imperative to reflect on the lessons of the past to ensure that we do not repeat these mistakes.
Moreover, there is a pressing need for policies that govern the use of BCIs and similar technologies. Ensuring ethical standards are established, including obtaining informed consent from all users, is vital for the responsible development of neurotechnology. As the technology matures, it can also foster advancements in mental health treatment and cognitive enhancement. However, the potential for unintended consequences means stakeholders must proactively safeguard against scenarios where these innovations could be weaponized to manipulate minds, effectively creating a new avenue for mind control.
The Market Potential of BCIs: A $400 Billion Opportunity
The market potential for brain-computer interfaces is staggering, with estimates suggesting it could surpass $400 billion in the U.S. The ability of BCIs to assist individuals with various forms of physical and cognitive disabilities opens new opportunities for healthcare technologies. As innovations proliferate, companies in the neurotechnology sector are racing to develop solutions that not only enhance human capabilities but also improve the quality of life for millions. This financial influx can drive research and development, leading to more refined BCIs that can be made accessible to a broader audience.
Yet, with immense commercial interest comes the challenge of ensuring that ethical considerations do not fall by the wayside. As companies prioritize profitability within the burgeoning neurotechnology market, the onus is on regulators and ethical boards to ensure the protection of end-users. Innovations must be paired with regulations to prevent potential exploitations in mental privacy and to establish frameworks addressing consent and rights over personal cognitive data, setting a precedent that aligns technological advancement with ethical responsibility.
Global Trends in Neurotechnology: How BCIs are Shaping the Future
Internationally, the application of brain-computer interfaces varies significantly, influenced by regional regulatory standards and cultural approaches to privacy and technology. In countries like China, for instance, devices that monitor brain activity in children have generated widespread concern. While such innovations aim to enhance focus and learning capabilities, they also raise ethical alarms about surveillance and consent among minors. This juxtaposition highlights the need for global dialogue about the ethical use of neurotechnology, especially as countries like the U.S. further invest in BCI research.
As BCIs gain traction on the international stage, collaboration and competition between nations could intensify. This dynamic emphasizes the importance of a shared ethical framework to guide development and implementation. Countries must work together to establish norms and safeguards that prioritize mental privacy while fostering innovation. The cooperative pursuit of ethical standards will be crucial in confronting potential abuses of BCI technology and addressing universal human rights concerns in an increasingly interconnected world.
Historical Lessons on Mind Control and Modern Neurotechnology
Reflecting on the grim history of mind control experiments reveals that the foundation of ethical standards in neurotechnology must be built on lessons learned from past abuses. The infamous MKUltra program highlighted how scientific advancements could be misused against individuals under the guise of national security. Today, as we embark on the era of brain-computer interfaces, there is a pressing responsibility to avoid repeating such mistakes. The necessity for transparency, accountability, and informed consent cannot be overstated, serving as a bulwark against the potential dark applications of BCI technology.
The echoes of these historical fears remain relevant as we explore the capabilities of advanced neurotechnology. Just as the Cold War ushered in experiments that sought to manipulate human behavior, the current capabilities of BCIs could lead us down a perilous path if mismanaged. Continuous dialogue among technologists, ethicists, and policymakers will be essential in shaping a future where innovation does not come at the expense of human rights or autonomy.
Mental Privacy in the Age of Brain-Computer Interfaces
As brain-computer interfaces become increasingly integrated into daily life, issues of mental privacy come to the forefront. The ability of BCIs to interpret and transmit brain signals presents a unique challenge: how do we protect individuals’ thoughts and mental processes from unauthorized access? With the rise of data privacy concerns in the digital age, it is critical to extend these concerns to neurotechnology. Safeguarding mental privacy involves establishing protocols that limit who can access and utilize this sensitive information, ensuring that users retain control over their cognitive data.
The debate surrounding mental privacy will only intensify as BCI technology advances. As researchers explore applications that decode thoughts or emotions, the ethical implications stretch into uncharted territories. Regulations must be crafted to prevent misuse by corporations or governmental entities, safeguarding individuals from intrusive data collection practices. Achieving a balanced approach that harnesses the benefits of neurotechnology while securing mental privacy is essential for fostering public trust and support for BCI adoption.
Future Innovations in Neurotechnology: Risks and Rewards
The future of neurotechnology and brain-computer interfaces is filled with both exciting possibilities and significant risks. Innovations may unlock unprecedented potential to enhance human cognition, assist in rehabilitation, and improve mental health treatments. However, as these technologies evolve, their applications may evoke ethical dilemmas akin to those faced during the Cold War. The race to develop superior neurotechnologies may inadvertently bring forth issues of mind control and psychological manipulation, highlighting the importance of setting boundaries.
Navigating the balance between innovation and ethical responsibility will be paramount in the coming years. While technological advancements could revolutionize fields like medicine and education, stakeholders must remain vigilant about the implications of their deployment. Critical discussions surrounding BCI technology must include diverse perspectives, ensuring that proactive measures are taken to prevent any potential negative outcomes that could echo the dark lessons of the past.
The Role of Legislation in Shaping Neurotechnology Development
Legislation plays a crucial role in guiding the ethical development and application of brain-computer interfaces and other neurotechnologies. As governments begin to create policies that govern the use of these technologies, it is vital to establish frameworks that prioritize user safety, mental privacy, and informed consent. By proactively addressing these issues within legislative parameters, the risks associated with BCI technologies can be mitigated effectively.
Moreover, as the neurotechnology sector continues to evolve rapidly, lawmakers must stay informed about technological advancements. Collaborations between technologists, ethicists, and legislators will ensure that regulations not only keep pace but also remain relevant amidst the dynamic landscape of BCI development. By prioritizing a robust ethical framework combined with thorough legislation, society can navigate the complexities of brain-computer interfaces while fostering innovation for the collective good.
Collaboration Between Tech Companies and Ethical Bodies
The development of brain-computer interfaces calls for a partnership between technology firms and ethical oversight bodies to navigate the implications of neurotechnology responsibly. As companies engage in the competitive race to innovate, collaboration with ethicists is vital for ensuring that developments reflect societal values and ethical standards. This dialogue can help instill confidence in the public regarding the safety and integrity of BCI applications, fostering trust in both the technology and the organizations behind it.
Such collaborations could also establish a set of best practices for the deployment and usage of BCIs. By prioritizing transparency and accountability, tech companies can create frameworks that respect user autonomy and safeguard against potential abuses of power. The shared expertise from both industries can lead to a well-rounded approach that balances technological advances with ethical considerations, ensuring that neurotechnology benefits society as a whole.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are brain computer interfaces (BCIs) and how do they function?
Brain computer interfaces (BCIs) are advanced neurotechnology systems that allow direct communication between a brain and an external device. BCIs work by detecting brain activity through sensors, usually implanted or placed on the scalp. This activity is then translated into commands that can control devices such as computers or prosthetic limbs, enabling individuals with disabilities to regain some autonomy.
What is the potential of BCI technology in medical applications?
BCI technology holds significant promise in the medical field, particularly for individuals with paralysis or neurological disorders. By connecting brain activity directly to assistive devices, BCIs can help users control prosthetic limbs or communicate through speech-generating devices. With a projected market of around $400 billion, the implications for improving life quality in patients with spinal cord injuries or strokes are enormous.
What ethical concerns are associated with brain chip implants?
The implementation of brain chip implants raises critical ethical concerns, particularly regarding mental privacy and consent. There are fears that BCIs could be exploited for mind control or unauthorized access to a person’s thoughts, reminiscent of historical abuses like the CIA’s MKUltra program. This necessitates careful regulation and ethical guidelines to protect individuals’ autonomy and mental integrity.
Can BCIs be used for mind control or psychological manipulation?
While the technology behind BCIs is primarily focused on therapeutic applications, there is a potential for misuse in mind control or psychological manipulation. Concerns are rising about future scenarios where BCIs could be employed by governments or private entities to influence thoughts or behaviors without consent, echoing past psychological experiments that sought to control human behavior.
What advancements are being made in neurotechnology related to BCIs?
Neurotechnology and BCIs are rapidly evolving, with ongoing research aimed at enhancing the precision and capabilities of brain chip implants. Advancements include improving signal clarity from the brain, developing non-invasive methods of brain signal monitoring, and integrating AI to interpret neural activity more accurately, thereby broadening their application spectrum.
How are brain-computer interfaces impacting society and technology?
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) are set to revolutionize both society and technology. By enabling new modes of interaction and control, BCIs are leading to innovations in assistive technologies, gaming, and even education. However, as these technologies become more pervasive, societal discourse on mental privacy and ethical implications surrounding their use is becoming increasingly important.
What are the risks involved with BCI technology?
While BCIs have the potential for groundbreaking benefits, they also carry risks such as the possibility of data breaches related to mental privacy, ethical concerns regarding consent for their use, and unintended psychological effects from stimulation. Moreover, misuse by state or corporate actors poses significant questions about accountability and user autonomy.
How does the market for BCI technology look in the coming years?
The market for brain-computer interface (BCI) technology is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, with estimates projecting it could reach around $400 billion in the U.S. alone. This growth will be driven by increasing demand for assistive devices, advancements in neurotechnology, and the need for innovative solutions in healthcare and rehabilitation.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| First Brain Chip Implant | Noland Arbaugh became the first recipient of a Neuralink brain chip implant, allowing him to control a computer mouse and play chess using his mind. |
| Potential Benefits of BCIs | BCIs could assist people with disabilities in controlling prosthetic limbs, communicating thoughts, and operating digital devices, with a potential market of $400 billion in the US. |
| Historical Warnings | A discussion paper highlights past misuse of mind control techniques during the Cold War, where unethical experiments were conducted to manipulate behavior. |
| Ethical Implications | Concerns about self-determination, consent, and mental privacy are raised, particularly regarding the ability to decode thoughts and potentially influence behavior. |
| Continued Development | Despite risks, there is support for advancing BCI technology to stay competitive against potential global threats. |
Summary
Brain computer interfaces (BCIs) represent groundbreaking advancements in technology that hold significant promise for transforming the lives of individuals with disabilities. However, as the development of this technology progresses, it is crucial to be mindful of historical lessons learned from past abuses in psychological experimentation. Attention to ethical implications regarding consent and mental privacy must guide the responsible advancement of BCIs to harness their benefits while safeguarding against potential misuse.